Comparing Efficiency of Various Powder Coating Techniques in Electrostatic Spray Application
Electrostatic powder coating is a widely utilized method for applying durable and high-quality finishes to a variety of surfaces. The efficiency of powder coating processes greatly influences productivity, cost-effectiveness, and the overall quality of the final product. In this article, we compare the efficiency of several powder coating techniques commonly used in electrostatic spray application.
-
-
Corona Charging
Corona charging is one of the traditional methods used in electrostatic powder coating. In this technique, the powder particles are charged by passing through a corona discharge generated by a high-voltage electrode. The charged particles are then attracted to the grounded workpiece, resulting in uniform coating deposition.
Efficiency:
- Pros: Corona charging is relatively simple and cost-effective, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. It offers good coverage and adhesion, especially on metal substrates.
- Cons: However, corona charging may produce more overspray compared to other methods, leading to lower transfer efficiency and increased material waste.
-
Tribocharging
Tribocharging involves imparting electrostatic charge to powder particles through frictional contact with a non-conductive material, such as a Teflon or nylon surface. The charged particles are then attracted to the grounded substrate, forming a uniform coating layer.
Efficiency:
- Pros: Tribocharging offers better transfer efficiency and reduced overspray compared to corona charging. It is particularly effective for coating complex shapes and non-metallic substrates.
- Cons: However, tribocharging systems tend to be more complex and expensive to implement. They may also require additional process optimization to achieve optimal coating quality.
-
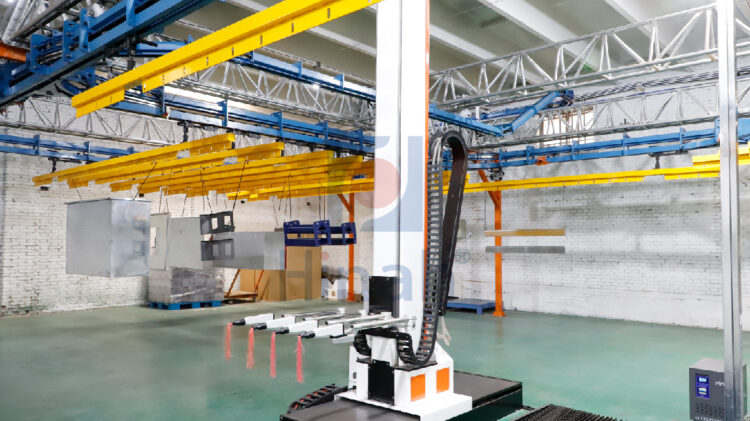

-
-
Electrostatic Disc Spraying
Electrostatic disc spraying utilizes a spinning disc to charge and propel powder particles towards the substrate. The disc generates an electrostatic field that charges the particles as they pass through it, ensuring uniform coating deposition.
Efficiency:
- Pros: Electrostatic disc spraying offers high transfer efficiency and precise control over coating thickness. It is suitable for both small and large-scale production environments, providing consistent results with minimal overspray.
- Cons: The initial investment cost for electrostatic disc spraying equipment may be higher compared to other methods. Additionally, maintenance and cleaning of the spraying disc are essential to prevent particle buildup and ensure continuous operation.
-
Corona-Assisted Fluidized Bed
In corona-assisted fluidized bed coating, powder particles are fluidized in a bed and charged using a corona discharge before being sprayed onto the substrate. This technique combines the advantages of fluidized bed coating with electrostatic charging for improved coating uniformity.
Efficiency:
- Pros: Corona-assisted fluidized bed coating offers excellent coating adhesion and coverage, particularly for irregularly shaped or porous substrates. It provides high transfer efficiency and minimal material waste.
- Cons: However, this method requires specialized equipment and may be less suitable for thin film applications or delicate substrates.
-
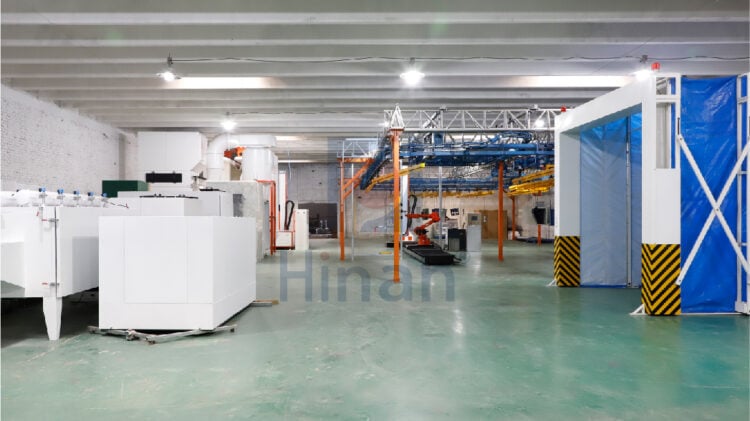

Conclusion
Each powder coating technique in electrostatic spray application offers unique advantages and limitations in terms of efficiency, coating quality, and suitability for different applications. While corona charging and tribocharging are traditional methods with their own merits, electrostatic disc spraying and corona-assisted fluidized bed coating represent advancements that offer higher transfer efficiency and improved coating uniformity. The choice of technique depends on factors such as substrate material, coating thickness requirements, production volume, and budget constraints. By understanding the characteristics of each method, manufacturers can select the most appropriate powder coating technique to achieve optimal efficiency and quality in their operations.






